Speech Therapy dj Sound

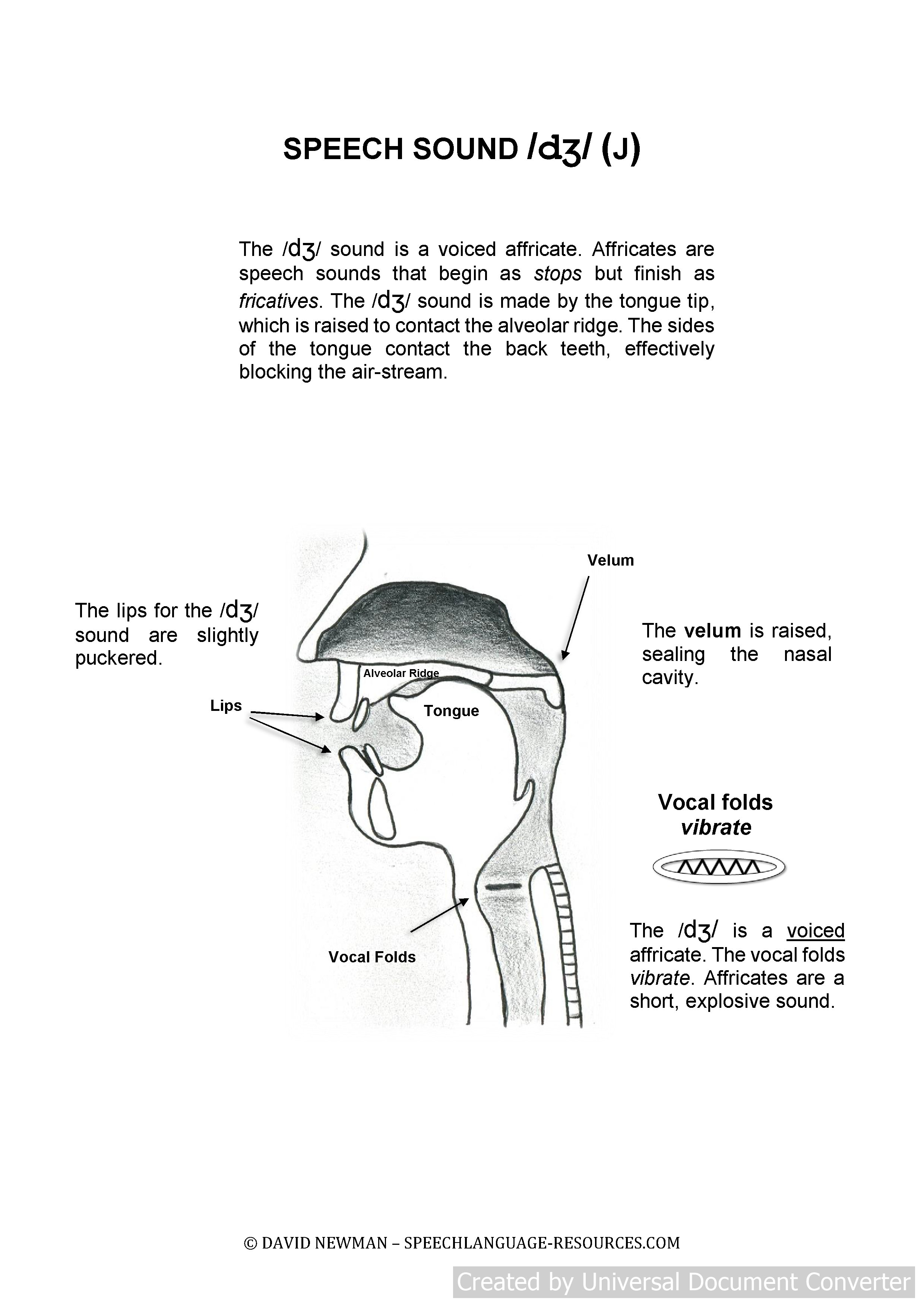
Speech Therapy dj Sound: The /dʒ/ sound is a voiced affricate. Affricates are speech sounds that begin as stops but finish as fricatives. The /dʒ/ phoneme is made by the tongue tip which is raised to contact the alveolar ridge. The sides of the tongue contact the back teeth, effectively blocking the air-stream.
The tongue tip is quickly lowered creating an explosive release of air across a broad area of constriction, which creates a short but windy voiced sound that has the same characteristics of a stop sound with some characteristics of a stream of air sound.
Speech Therapy dj Sound - /dʒ/ Sound errors and Sound Stimulation
The most common speech sound error involving the /dʒ/ sound is when the /dʒ/ becomes the /d/ sound. Jump becomes dump and June becomes dune, etc.
How to stimulate the/dʒ/ sound
Demonstrate the characteristics of correct /dʒ/ production to your child.
- For the /dʒ/ sound the blade of the tongue is at the rear of the oral cavity touching the upper back teeth.
- The vocal folds vibrate.
- The air-stream passes through the centre of the oral cavity over the shal-low valley between the tongue and the roof of the mouth.
- The lips stick out slightly.
- The sound is mostly a stop and is short in nature.
Speech Therapy dj Sound - /dʒ/ Sound stimulation
Work through the following procedures with your child.
- Raise your tongue so that you can feel the upper teeth at the back of the mouth.
- Touch the tongue tip at the roof of the mouth then lower it so that it doesn’t touch any structure in the mouth. The tongue should feel like it is in the middle of the mouth.
- Pucker your lips.
- Allow the air-stream to flow over the centre or the middle of the tongue. The sound is voiced.
- In contrast to the /ʒ/ sound the /dʒ/ sound is short and explosive.
Speech Therapy dj - Sculpting Sound from other Speech Sounds
Many speech sounds can be sculpted using other speech sounds as a starting point. This involves altering or adjusting speech sounds so that they approach the target sound in nature. This works by the clinician modeling a sound that the child is able to produce. The clinician then makes slight, progressive adjustments to the sound until the target sound is generated.
Sound sculpting from the /d/ and /ʒ/ sound sounds
The /dʒ/ sound can be formed from the /d/ and /ʒ/ sounds. We do this by first shaping our mouth for the /ʒ/ sound. We then produce a sustained /ʒ/ sound. We then raise the tongue so that it touches the alveolar ridge then a build-up of pressure from the tongue blocking the pharynx.
Next, pucker the lips slightly.
Release tongue. The sound is a short, explosive sound, the /dʒ/ sound.
Sound sculpting from the /n/ sound
- The /dʒ/ sound can be formed from the /n/ sound. We do this by first shaping our mouth for the /n/ sound. We do this by touching our tongue tip to the roof of the mouth (alveolar ridge). We produce a sustained /n/ sound then lower the tongue a little while building up pressure with the tongue blocking the back of the mouth.
- Next, pucker the lips slightly.
- Release the tongue. The sound should be a short, explosive sound, the /dʒ/ sound.
Updated 13/08/2020