Norm Referenced Assessment
Norm referenced Assessment: Standardized tests are norm referenced and considered to be formal language assessments.
Standardized tests are generally well constructed and give an accurate and meaningful picture of a child's oral language
skills compared to children of the same age. That is, during the tests construction the norm referenced assessment sub-tests are administered to a wide variety of children, most of whom have typically developing language skills.
Children with poor language skills
produce lower than average scores on standardized assessments, as compared to their typically developing peers
who performed well on the test.
Standardized tests have the following attributes:
Clear administration and scoring criteria: The assessment is always given in the same manner and always scored the same way.
Validity: The tests are valid. That is, there is little systematic error or bias.
Reliability: An assessment is considered reliable if its measurements are consistent.
Standardization: A sample of individuals in a particular age group needs to be big enough so that accurate
and reliable statistical conclusions can be recorded. A minimum of at least 100 people is required and people should be gathered from several geographic areas, with both females and males represented in the sample.
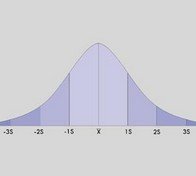 Measures of central tendency and variability: A bell-shaped curve is a visual representation that is used to form a normal distribution of how people have performed on a particular assessment.
Measures of central tendency and variability: A bell-shaped curve is a visual representation that is used to form a normal distribution of how people have performed on a particular assessment.
To use an analogy, a bell shaped curve looks a little like a steep-sided hill. Most scores in a sample will fall close to the mean, which is the line in the center of the hill, or the top of the hill.
The two sloping flanks of the hill represent the people who produced scores lower than average (scores on the left) and the people
who produced higher than average (scores on the right). The scores of people who performed very poorly on the test are distributed on the far left flank of the hill, where the ground is almost flat. On the far, opposite flank of the hill are distributed the scores of people who performed exceptionally well on the test.
Standard error of measurement: Norm referenced assessment sub-tests contain standard errors of measurement. Measurement errors are to be expected because human beings are never constant in their behaviour. Standard errors of measurement are used to estimate a confidence interval.
Norm-referenced scores: An individual's tallied raw score on a test is compared to other raw scores of all the subjects who
performed on the test during the test's initial construction and development. Each standardized test has a norms table where a client's raw scores are converted to a standard score.
Standardized assessments are critically important in identifying language disorder in school-age children. They are vital because they
accurately and reliably establish whether a child's language skills are developing as well as same age peers.
Standardized tests are limited
however when it comes to planning effective oral and written language intervention. Other, more specific, assessments can be utilized to plan for intervention.
The most prominent of these assessment tools are criterion referenced assessments.
References
Kaderavek, J.N. (2011) Language Disorders in Children: Fundamental Concepts of Assessment and Intervention, Allyn & Bacon
Paul, R. (2006) Language Disorders from Infancy through Adolescence. Assessment and Intervention. Mosby
Content Updated 10/11
Return from Norm Referenced Assessment to Speech Language Assessment
Enjoy this page? Please pay it forward. Here's how...
Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment,
your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.
|